Different ways of utilizing Vue.
Vue can be used to control parts of HTML pages or entire pages .
- Widget approach on a multi-page application.
Vue can also be used to control the entire frontend of a web application.
- SPA approach – Server only sends one HTML page, thereafter, Vue takes over and controls the UI.
{{ }} -> interpolation syntax
Vue renders the data using the interpolation syntax, it can render Strings, Numbers, Booleans, Arrays, Objects etc.
Interpolation syntax can also render JavaScript expressions.
<body>
<header>
<h1>Vue Course Goals</h1>
</header>
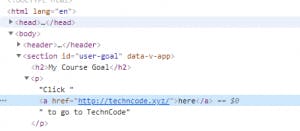
<section id="user-goal">
<h2>My Course Goal</h2>
<p>{{courseGoal}}</p>
<p>{{stringVar}}</p>
<p>{{numberVar}}</p>
<p>{{boolVar}}</p>
<p>{{arrayVar}}</p>
<p>{{objectVar}}</p>
<p>{{3+4}}</p>
</section>
</body>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
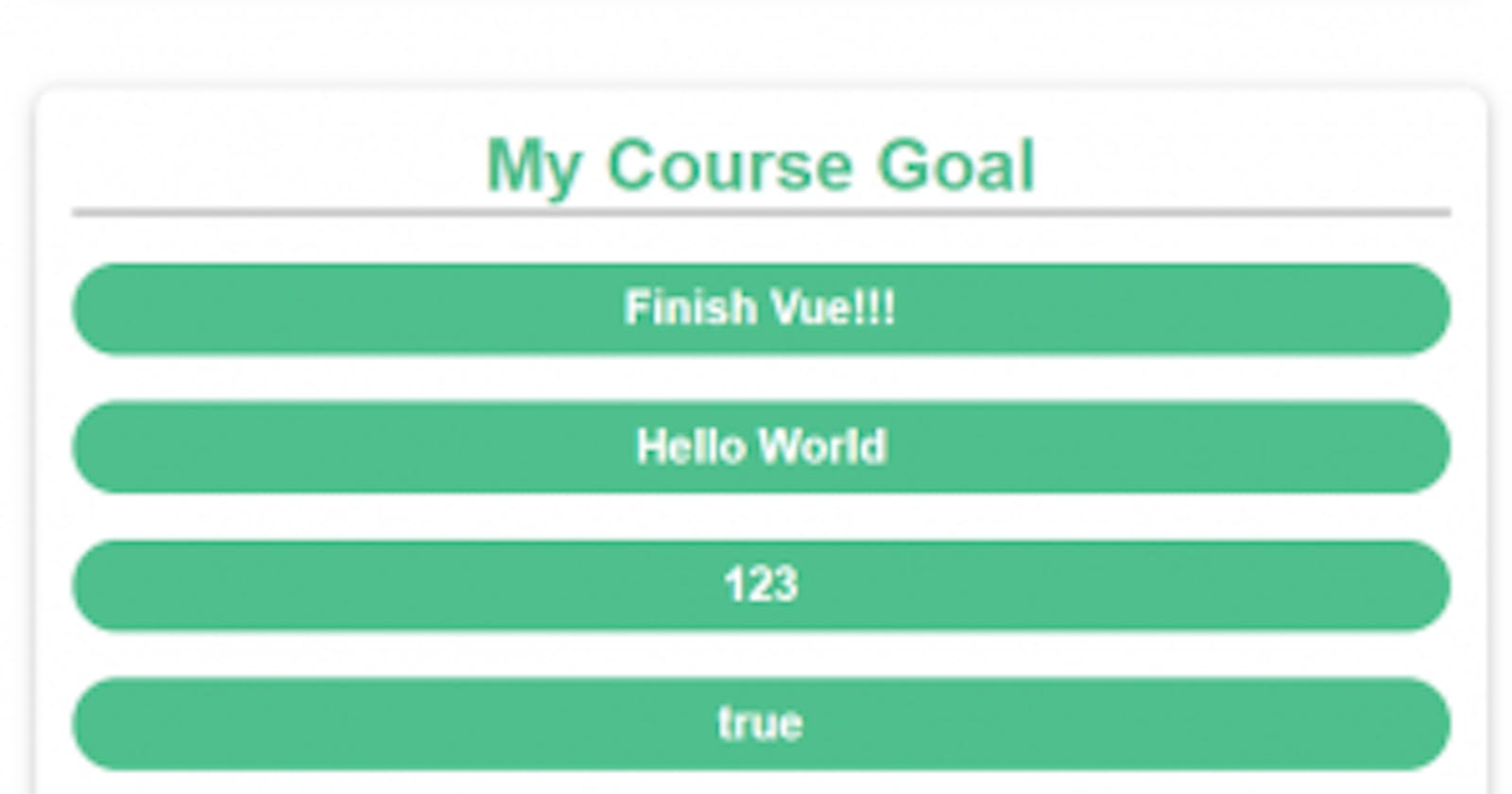
courseGoal: "Finish Vue!!!",
stringVar: "Hello World",
numberVar: 123,
boolVar: true,
arrayVar: [99, 100, 100],
objectVar: { name: "John" },
};
},
});
app.mount("#user-goal");
 Vue – interpolation
Vue – interpolation
createApp creates a Vue instance which is mount on a certain part of the html page (some div) or the entire page (body), denoted by a CSS selector.
createApp takes in an object – which has a data function – that further returns an object. This data function name can not be altered, under the hood Vue sees the data function and does the necessary stuffs.
Vue.createApp({ // createApp takes in an object
data() { // data function
return {}; // returns an object
},
});
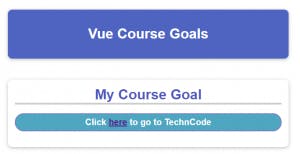
v-bind directive:
v-bind directive helps to bind to html attributes, ex: href, src etc.
<body>
<header>
<h1>Vue Course Goals</h1>
</header>
<section id="user-goal">
<h2>My Course Goal</h2>
<p>Click <a v-bind:href="link">here</a> to go to TechnCode</p>
</section>
</body>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
courseGoal: "Finish Vue!!!",
link: "http://techncode.xyz/",
};
},
});
app.mount("#user-goal");
 v-bind directive
v-bind directive